CPM: Stem to Stern
The concept of going entirely thru a project from beginning to ending is fundamental to CPM and to the Diagonal Method, which uses CPM. In the Navy, the stem is the frontmost part of the ship and the stern is the rearmost part. Over the centuries, many of the Ramage family have been sailors and the phrase stem to stern has been common in our speech patterns.
Failure to follow the critical path from stem to stern thru the project is catastrophic, absurd, and stupid. At the AQMD, the manager and the designers of the Expansion Project became so tired in writing the specifications that they skipped an essential middle section that describe the daily processors. No one made sure that a path existed from stem to stern.
Longest and Shortest Paths
By definition of the CPM algorithm, the first complete path from stem to stern is the initial critical path and the initial shortest ROI. The next path might replace either. The manager persists in analyzing all of the paths; for each path, the manager keeps the duration, which determines its rank relative to the other paths. Each path ends at the completion of implementation; not only is part of the project done, but that part has been installed. A program belongs to a project, but the program itself is only a fraction of the part; the program is a task along a path. See Work Units
Failure to follow the critical path from stem to stern thru the project is catastrophic, absurd, and stupid. At the AQMD, the manager and the designers of the Expansion Project became so tired in writing the specifications that they skipped an essential middle section that describe the daily processors. No one made sure that a path existed from stem to stern.
Longest and Shortest Paths
By definition of the CPM algorithm, the first complete path from stem to stern is the initial critical path and the initial shortest ROI. The next path might replace either. The manager persists in analyzing all of the paths; for each path, the manager keeps the duration, which determines its rank relative to the other paths. Each path ends at the completion of implementation; not only is part of the project done, but that part has been installed. A program belongs to a project, but the program itself is only a fraction of the part; the program is a task along a path. See Work Units
|
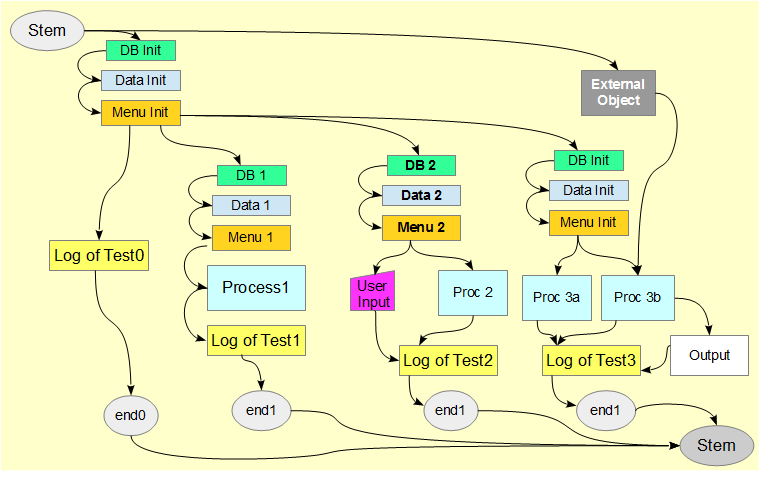
The chart starts with Stem; there are four overviews.
The designer chose to emphasize the data base, data, and menu parts of the chart. Each of the four groups displays but a few paths; however, within the boxes, many more paths and boxes could exist. Because of the potential for concurrent actions, more than one path might be active at once. Path0 must provide some measurable change, so it probably alters the data base or access to the data base. In this example, the chart shows an overview of a project. The chart is meant to hold ideas in relative positions. Other charts explain text. |
The chart ends at Stern. The external object represents all kinds of possible items and actions from outside the typical data processing
Each of the Logs of Tests preserves the results and the interactions of the module with previous modules. Each of the paths represents a major kind of path; there are many other kinds. A process can represent many kinds of transactions. The chart should accurately portray the relationships chosen by the manager and designers. The corresponding list should be considered the primary source. The list contains the numbers. |